Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Routes.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. The structure of tables comprising core Routes data didn't change, however the data model related to resource requirements did change and was enhanced. Please note that after you import Routes you may need to perform approval and activation of Route and Route versions, this can also be done as a part of initial import.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (RouteTable, RouteVersion, Route) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Routes. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
RouteTable
|
The RouteTable table contains routes, which in turn contain information that is required to guide an item through production. Each route includes operations to perform, the sequence for the operations, resources involved in completing the operations, and standard times for the setup and run of the production.
|
RouteVersion
|
The RouteVersion table contains versions for the routes defined in the RouteTable table. A route version connects to a route and additionally has parameters that define whether the route version is valid from a certain date or for a certain quantity. A route version needs to be approved to be used. Therefore, each route version record is started and approved by the property that is stored.
|
Route
|
The Route table contains the operations that represent the routes. Each record contains information about an operation that belongs to a route. Each operation connects to an operation stored in the RouteOprTable table.
|
Data model diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromSalesTable method on SalesLine table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
One prerequisite that I’ll need for import is to assign a worker to my current AX User, this is needed because I’ll approve and activate BOM and BOM Version right after their creation
User – User relations
Source code:
static void RouteXppImport(Args _args)
{
RouteTable routeTable;
RouteVersion routeVersion;
Route route;
Route routePrevious;
RouteOpr routeOpr;
InventDim inventDim;
RouteApprove routeApprove;
RouteVersionApprove routeVersionApprove;
RouteVersionActivate routeVersionActivate;
ItemId itemId = "D0001";
RouteId routeId;
OprNum oprNum;
OprNumNext oprNumNext;
RouteOprId oprId = "Testing";
RouteOprId nextOprId;
RouteAccErrorPct accError;
RouteOprPriority oprPriority;
RouteErrorPct errorPct;
SchedJobLinkType linkType;
JmgJobPayType payType;
RouteOprTimeQueueBefore queueTimeBefore;
RouteOprTimeSetup setupTime;
RouteOprTimeProcess processTime = 1;
RouteOprQtyProcessNumOf processPerQty;
RouteOprTimeTransport transpTime;
RouteOprTimeQueueAfter queueTimeAfter;
RouteOprQtyTransferBatch transferBatch;
RouteHourFactor toHours;
RouteCostCategoryIdSetup setupCategoryId;
RouteCostCategoryIdProcess processCategoryId;
RouteCostCategoryIdQty qtyCategoryId;
RouteOprType routeOprType;
PropertyId propertyId;
RouteGroupId routeGroupId = "Proc";
RouteFormulaFactor formulaFactor1;
RouteFormula formula;
WrkCtrIdCost wrkCtrIdCost;
RefRecId activity;
InventSiteId siteId = "1";
RouteId newRouteId()
{
NumberSeq numberSeq;
;
numberSeq = RouteTable::numberSeq();
numberSeq.used();
return numberSeq.num();
}
OprNum findMaxOprNum(RouteId _routeIdTmp)
{
Route routeTmp;
select maxof(OprNum) from routeTmp
where routeTmp.RouteId == _routeIdTmp;
return routeTmp.OprNum;
}
;
ttsBegin;
routeId = newRouteId();
routeTable.clear();
routeTable.initValue();
routeTable.RouteId = routeId;
routeTable.Name = "Alex" + routeId;
routeTable.ItemGroupId = InventTable::find(itemId).itemGroupId();
//routeTable.Approved = NoYes::Yes;
//routeTable.Approver = HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId());
if (routeTable.validateWrite())
{
routeTable.insert();
routeVersion.clear();
routeVersion.initValue();
routeVersion.ItemId = itemId;
//routeVersion.Approved = NoYes::Yes;
//routeVersion.Approver = HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId());
//routeVersion.Active = NoYes::Yes;
routeVersion.initFromRouteTable(routeTable);
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = siteId;
routeVersion.InventDimId = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).inventDimId;
if (routeVersion.validateWrite())
{
routeVersion.insert();
route.clear();
route.initValue();
// update previous operation which has their next operation set to the current operation
select firstonly forupdate routePrevious
index hint OperationIdx
order by routePrevious.OprNum desc
where routePrevious.RouteId == routeId;
route.RouteId = routeTable.RouteId;
if (oprNum)
{
route.OprNum = oprNum;
}
else
{
if (route.OprNum == 0)
{
route.OprNum = findMaxOprNum(routeTable.RouteId) + 10;
route.write();
}
}
if (routePrevious.RecId != 0 && routePrevious.OprNumNext == 0)
{
routePrevious.OprNumNext = route.OprNum;
routePrevious.update();
}
if (oprNumNext)
{
route.OprNumNext = oprNumNext;
}
else
{
if (nextOprId)
{
route.OprNumNext = findMaxOprNum(routeTable.RouteId) + 10;
}
}
if (oprId)
route.OprId = oprId;
route.AccError = accError;
route.OprPriority = oprPriority;
route.ErrorPct = errorPct;
route.LinkType = linkType;
route.JobPayType = payType;
routeOpr.clear();
routeOpr.initValue();
routeOpr.OprId = oprId;
routeOpr.QueueTimeBefore = queueTimeBefore;
routeOpr.SetupTime = setupTime;
routeOpr.ProcessTime = processTime;
routeOpr.ProcessPerQty = processPerQty;
routeOpr.TranspTime = transpTime;
routeOpr.QueueTimeAfter = queueTimeAfter;
routeOpr.TransferBatch = transferBatch;
routeOpr.ToHours = toHours;
routeOpr.SetUpCategoryId = setupCategoryId;
routeOpr.ProcessCategoryId = processCategoryId;
routeOpr.QtyCategoryId = qtyCategoryId;
routeOpr.RouteType = routeOprType;
routeOpr.PropertyId = propertyId;
routeOpr.RouteGroupId = routeGroupId;
routeOpr.FormulaFactor1 = formulaFactor1;
routeOpr.Formula = formula;
routeOpr.WrkCtrIdCost = wrkCtrIdCost;
routeOpr.RouteCode = RouteAll::Route;
routeOpr.RouteRelation = route.RouteId;
routeOpr.ItemCode = TableGroupAll::Table;
routeOpr.ItemRelation = itemId;
routeOpr.SiteId = siteId;
if (route.validateWrite())
{
route.write();
}
if (routeOpr.validateWrite())
{
routeOpr.write();
}
}
}
ttsCommit;
if (routeTable)
{
routeApprove = routeApprove::newRouteTable(routeTable);
routeApprove.parmApprover(HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId()));
routeApprove.run();
}
if (routeVersion)
{
routeVersionApprove = BOMRouteVersionApprove::newRouteVersion(routeVersion);
routeVersionApprove.parmApproveRoute(true);
routeVersionApprove.parmRemove(false);
routeVersionApprove.parmApprover(HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId()));
routeVersionApprove.run();
routeVersionActivate = BOMRouteVersionActivate::newRouteVersion(routeVersion);
routeVersionActivate.run();
}
}
|
Result:
Infolog
Please note the infolog which indicates that cost categories have not been assigned and no resource requirements have been specified. You can modify the script above to handle cost categories, in fact it would take a longer effort to accommodate for resource requirements of desired type (resource type, resource group, resource, capability, skill, course, certificate, title)
Route
Please note that I removed approval and activation from the existing Route Version prior to importing a new one to avoid overlap (based on dates/dimensions) validation error
Route details
Please note that you can create your Route structure once and then assign to a different Route Versions (for different items) multiple times. Or you may choose to create a new Route structure for each Route Version (for particular item) depending on your business requirements
Route
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2, R3
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Routes. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Routes.
Author: Alex Anikiev, PhD, MCP
Tags: Dynamics ERP, Dynamics AX 2012, X++, Xpp, Data Import, Data Conversion, Data Migration, Routes
Note: This document is intended for information purposes only, presented as it is with no warranties from the author. This document may be updated with more content to better outline the concepts and describe the examples.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp – BOMs Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import BOMs (Bill of materials).
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. However the structure of tables comprising BOMs didn't change. Please note that after you import BOMs you may need to perform approval and activation of BOM and BOM versions, this can also be done as a part of initial import.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (BOMTable, BOMVersion, BOM) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import BOMs. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
BOMTable
|
The BOMTable table contains all of the bills of materials. A bill of materials is associated with a site and an item group. For each bill of materials, the information is stored about whether it has been approved and by whom.
|
BOMVersion
|
The BOMVersion table contains all the BOM versions. This table connects to the BOMTable table in order to specify the BOM to which the version refers, and it connects to the InventTable table to specify to which item the BOM version is assigned. The BOMVersion table also connects to the InventDim table to specify a site for the BOM version. Additionally, the BOMVersion table stores information about the approval and activation for each BOM version.
|
BOM
|
The BOM table contains the bill of materials lines. A BOM line connects to an item to consume and a BOM version to which the line applies.
|
Data model diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromSalesTable method on SalesLine table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
One prerequisite that I'll need for import is to assign a worker to my current AX User, this is needed because I'll approve and activate BOM and BOM Version right after their creation
User – User relations
Source code:
static void BOMXppImport(Args _args)
{
BOMTable bomTable;
BOMVersion bomVersion;
BOM bom;
InventDim inventDim;
BOMApprove bomApprove;
BOMVersionApprove bomVersionApprove;
BOMVersionActivate bomVersionActivate;
BOMId bomId;
BOMEndSchedConsump bomEndSchedConsump;
ProdFlushingPrincipBOM prodFlushingPrincip;
WrkCtrConsumption wrkCtrConsumption;
BOMType bomType;
BOMConsumpType bomConsumpType;
ItemId itemId = "D0001", bomItemId = "M0001";
BOMQty bomQty = 1;
NoYes calculation;
BOMMeasureHeight height;
BOMMeasureWidth width;
BOMMeasureDepth depth;
BOMMeasureDensity density;
BOMMeasureConstant constant;
BOMRoundUp bomRoundUp;
BOMRoundUpQty bomRoundUpQty;
BOMPosition position;
OprNumBOM oprNum;
StartDate fromDate = today();
EndDate todate = today();
VendAccount vendId;
UnitOfMeasureSymbol unitID = "ea";
ConfigGroupId configGroupId;
BOMFormula bomFormula;
BOMQtySerie bomQtySerie;
ItemBOMId itemBOMId;
ItemRouteId itemRouteId;
PBAId itemPBAId;
ScrapVar scrapVar;
ScrapConst scrapConst;
InventDimId inventDimId = InventDim::inventDimIdBlank();
InventSiteId siteId = "1";
InventLocationId warehouseId = "11";
BOMId newBOMId()
{
NumberSeq numberSeq;
;
numberSeq = BOMTable::numberSeq();
numberSeq.used();
return numberSeq.num();
}
;
ttsBegin;
bomId = newBOMId();
bomTable.clear();
bomTable.initValue();
bomTable.bomId = bomId;
bomTable.SiteId = siteId;
bomTable.Name = "Alex" + bomId;
bomTable.ItemGroupId = InventTable::find(itemId).itemGroupId();
//bomTable.Approved = NoYes::Yes;
//bomTable.Approver = HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId());
if (bomTable.validateWrite())
{
bomTable.insert();
bomVersion.clear();
bomVersion.initValue();
bomVersion.ItemId = itemId;
//bomVersion.Approved = NoYes::Yes;
//bomVersion.Approver = HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId());
//bomVersion.Active = NoYes::Yes;
bomVersion.initFromBOMTable(bomTable);
if (bomVersion.validateWrite())
{
bomVersion.insert(false);// do not check for circularity
bom.clear();
bom.initValue();
bom.bomId = bomId;
bom.LineNum = BOM::lastLineNum(bomId) + 1;
bom.EndSchedConsump = bomEndSchedConsump;
bom.ProdFlushingPrincip = prodFlushingPrincip;
bom.WrkCtrConsumption = wrkCtrConsumption;
bom.bomConsump = bomConsumpType;
bom.initFromInventTable(InventTable::find(bomItemId));
bom.bomType = bomType;
bom.bomQty = bomQty;
bom.Calculation = NoYes::Yes;
bom.Height = height;
bom.Width = width;
bom.Depth = depth;
bom.Density = density;
bom.Constant = constant;
bom.RoundUp = bomRoundUp;
bom.RoundUpQty = bomRoundUpQty;
bom.Position = position;
bom.OprNum = oprNum;
bom.FromDate = fromDate;
bom.ToDate = todate;
bom.VendId = vendId;
bom.UnitId = unitID;
bom.ConfigGroupId = configGroupId;
bom.Formula = bomFormula;
bom.bomQtySerie = bomQtySerie;
bom.ItemBOMId = itemBOMId;
bom.ItemRouteId = itemRouteId;
bom.ItemPBAId = itemPBAId;
bom.ScrapVar = scrapVar;
bom.ScrapConst = scrapConst;
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = siteId;
inventDim.InventLocationId = warehouseId;
bom.InventDimId = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).inventDimId;
if (bom.validateWrite())
{
bom.insert();
}
}
}
ttsCommit;
if (bomTable)
{
bomApprove = bomApprove::newBOMTable(bomTable);
bomApprove.parmApprover(HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId()));
bomApprove.run();
}
if (bomVersion)
{
bomVersionApprove = BOMRouteVersionApprove::newBOMVersion(bomVersion);
bomVersionApprove.parmApproveBOM(true);
bomVersionApprove.parmRemove(false);
bomVersionApprove.parmApprover(HcmWorker::userId2Worker(curUserId()));
bomVersionApprove.run();
bomVersionActivate = BOMRouteVersionActivate::newBOMVersion(bomVersion);
bomVersionActivate.run();
}
}
|
Result:
BOM line
Please note that I removed approval and activation from the existing BOM Version prior to importing a new one to avoid overlap (based on dates/dimensions) validation error
BOM
Please note that you can create your BOM structure once and then assign to a different BOM Versions (for different items) multiple times. Or you may choose to create a new BOM structure for each BOM Version (for particular item) depending on your business requirements
BOM line
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2, R3
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import BOMs. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of BOMs.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Sales Orders Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Sales orders.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. However the structure of tables comprising Sales order header/lines didn't change. Please note that after you import Sales orders you may need to perform full/partial Physical and/or Financial update if required (for example, for Purchase orders already in execution).
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (SalesTable, SalesLine) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Sales orders. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
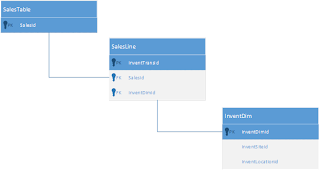
SalesTable
|
The SalesTable table contains all sales order headers regardless of whether they have been posted.
|
SalesLine
|
The SalesLine table contains all sales order lines regardless of whether they have been posted.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromSalesTable method on SalesLine table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void SalesOrdersXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Customer("US-001")
#define.DeliveryDate("1/1/2014")
#define.ItemId("M0001")
#define.Qty(10)
#define.Unit("ea")
SalesTable salesTable;
SalesLine salesLine;
InventDim inventDim;
try
{
ttsbegin;
//Order header
salesTable.clear();
salesTable.initValue(SalesType::Sales);
salesTable.SalesId = NumberSeq::newGetNum(SalesParameters::numRefSalesId()).num();
salesTable.DeliveryDate = str2Date(#DeliveryDate, 213);
salesTable.CustAccount = #Customer;
salesTable.initFromCustTable();
if (salesTable.validateWrite())
{
salesTable.insert();
//Order line
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = "1";
inventDim.InventLocationId = "12";
salesLine.clear();
salesLine.initValue(salesTable.SalesType);
salesLine.initFromSalesTable(salesTable);
salesLine.ItemId = #ItemId;
salesLine.initFromInventTable(InventTable::find(#ItemId));
salesLine.InventDimId = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).inventDimId;
salesLine.SalesQty = #Qty;
salesLine.RemainSalesPhysical = salesLine.SalesQty;
salesLine.SalesUnit = #Unit;
salesLine.QtyOrdered = salesLine.calcQtyOrdered();
salesLine.RemainInventPhysical = salesLine.QtyOrdered;
salesLine.setPriceDisc(InventDim::find(salesLine.InventDimId));
if (salesLine.validateWrite())
{
salesLine.insert();
}
else
throw error("Order line");
}
else
throw error("Order header");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Please note that I assign SalesId programmatically from Number sequence
Product – Sales price
Sales order header
Sales order lines
Packing Slip
Invoice
Inventory transactions
Physical Voucher
Financial Voucher
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Sales orders. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Sales orders.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Purchase Orders Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Purchase orders.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. However the structure of tables comprising Purchase order header/lines didn't change. Please note that after you import Purchase orders you may need to perform full/partial Physical and/or Financial update if required (for example, for Purchase orders already in execution).
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (PurchTable, PurchLine) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Sales orders. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
PurchTable
|
The PurchTable table contains all the purchase order headers regardless of whether they have been posted.
|
PurchLine
|
The PurchLine table contains all purchase order lines regardless whether they have been posted or not.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromPurchTable method on PurchLine table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void PurchaseOrdersXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Vendor("US-101")
#define.DeliveryDate("1/1/2014")
#define.ItemId("M0001")
#define.Qty(10)
#define.Unit("ea")
PurchTable purchTable;
PurchLine purchLine;
InventDim inventDim;
try
{
ttsbegin;
//Order header
purchTable.clear();
purchTable.initValue(PurchaseType::Purch);
purchTable.PurchId = NumberSeq::newGetNum(PurchParameters::numRefPurchId()).num();
purchTable.DeliveryDate = str2Date(#DeliveryDate, 213);
purchTable.initFromVendTable(VendTable::find(#Vendor));
if (purchTable.validateWrite())
{
purchTable.insert();
//Order line
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = "1";
inventDim.InventLocationId = "12";
purchLine.clear();
purchLine.initValue(purchTable.PurchaseType);
purchLine.initFromPurchTable(purchTable);
purchLine.initFromInventTable(InventTable::find(#ItemId));
purchLine.InventDimId = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).inventDimId;
purchLine.PurchQty = #Qty;
purchLine.RemainPurchPhysical = purchLine.PurchQty;
purchLine.PurchUnit = #Unit;
purchLine.QtyOrdered = purchLine.calcQtyOrdered();
purchLine.RemainInventPhysical = purchLine.QtyOrdered;
purchLine.setPriceDisc(InventDim::find(purchLine.InventDimId));
if (purchLine.validateWrite())
{
purchLine.insert();
}
else
throw error("Order line");
}
else
throw error("Order header");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Please note that I assign PurchId programmatically from Number sequence
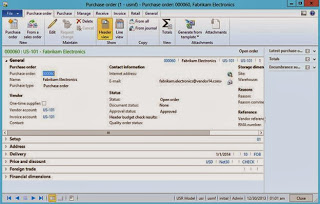
Purchase order header
Purchase order lines
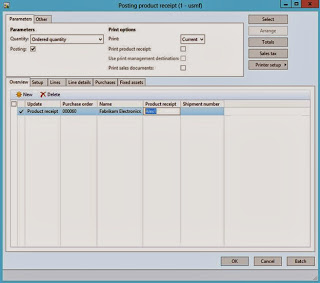
Product Receipt
Vendor Invoice
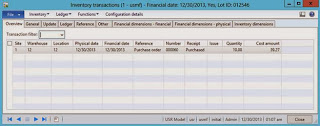
Inventory transactions
Physical Voucher
Financial Voucher
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Purchase orders. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Purchase orders.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Transfer Orders Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Transfer orders.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. However the structure of tables comprising Transfer order header/lines didn't change. Please note that after you import Transfer orders you may need to perform Ship and Receive operations if required (for example, for Transfer orders already in execution).
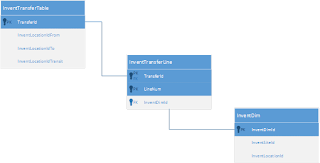
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (InventTransferTable, InventTransferLine) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Transfer orders. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
InventTransferTable
|
The InventTransferTable table contains information about transfer orders.
|
InventTransferLine
|
The InventTransferLine table contains information about items that are transferred from one warehouse to another by using a transfer order.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromInventTransferTable method on InventTransferLine table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void TransferOrdersXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.WarehouseFrom("11")
#define.WarehouseTo("12")
#define.ShipDate("1/1/2014")
#define.ReceiveDate("1/1/2014")
#define.ItemId("M0001")
#define.Qty(1)
#define.Site("1")
#define.Warehouse("11")
InventTransferTable inventTransferTable;
InventTransferLine inventTransferLine;
InventDim inventDim;
try
{
ttsbegin;
//Order header
inventTransferTable.clear();
inventTransferTable.initValue();
inventTransferTable.TransferId = InventTransferTable::numberSeq().num();
inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdFrom = #WarehouseFrom;
inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdTo = #WarehouseTo;
inventTransferTable.DlvModeId = CustVendTransportPointLine::defaultDeliveryMode(inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdFrom,'','','','',inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdTo);
inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdTransit = InventLocation::find(inventTransferTable.InventLocationIdFrom).InventLocationIdTransit;
inventTransferTable.initFromAddress();
inventTransferTable.initToAddress();
inventTransferTable.ShipDate = str2Date(#ShipDate, 213);
inventTransferTable.ReceiveDate = str2Date(#ReceiveDate, 213);
if (inventTransferTable.validateWrite())
{
inventTransferTable.insert();
//Order line
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = "1";
inventDim.InventLocationId = "12";
inventTransferLine.clear();
inventTransferLine.initValue();
inventTransferLine.ItemId = #ItemId;
inventTransferLine.InventDimId = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).inventDimId;
inventTransferLine.QtyTransfer = #Qty;
inventTransferLine.initFromInventTableModule(InventTableModule::find(inventTransferLine.ItemId,ModuleInventPurchSales::Invent));
inventTransferLine.QtyRemainReceive = inventTransferLine.QtyTransfer;
inventTransferLine.QtyRemainShip = inventTransferLine.QtyTransfer;
inventTransferLine.ShipDate = str2Date(#ShipDate, 213);
inventTransferLine.ReceiveDate = str2Date(#ReceiveDate, 213);
inventTransferLine.initFromInventTransferTable(inventTransferTable, false);
inventTransferLine.LineNum = InventTransferLine::lastLineNum(inventTransferLine.TransferId) +1.0;
if (inventTransferLine.validateWrite())
{
inventTransferLine.insert();
}
else
throw error("Order line");
}
else
throw error("Order header");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
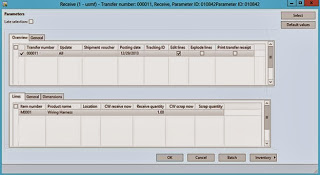
Result:
Warehouse
Please note that Transit Warehouse is assigned on From Warehouse record
Transfer order header and lines
Ship
Receive
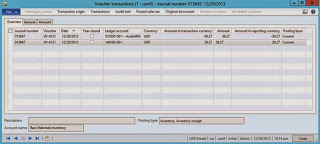
Inventory transactions
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Transfer orders. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Transfer orders.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Inventory Transactions Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Inventory transactions.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. However the structure of tables comprising Inventory journal header/lines didn't change as well as the structure of tables for inventory transactions. The proven method to import inventory transactions in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 is to import the data into Inventory journals and then validate/post the journals which will generate all necessary inventory and financial transactions.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (InventJournalTable, InventJournalTrans) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Inventory transactions. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
InventJournalTable
|
The InventJournalTable table contains information about inventory journals. The table holds information about how the journal is handled by the system.
|
InventJournalTrans
|
The InventJournalTrans table contains information about items and represents a line in an inventory journal. Each record has information related to a specific item and is related to a record in the InventJournalTable table, which is the journal header.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromInventJournalTable method on InventJournalTrans table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void InventoryTransactionsXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Description("Alex")
#define.ItemId("M0001")
#define.Qty(10)
#define.Site("1")
#define.Warehouse("11")
InventJournalTable inventJournalTable;
JournalTableData journalTableData;
InventJournalTrans inventJournalTrans;
JournalTransData journalTransData;
InventDim inventDim;
LineNum lineNum;
try
{
ttsbegin;
//Journal header
journalTableData = JournalTableData::newTable(inventJournalTable);
inventJournalTable.clear();
inventJournalTable.initValue();
inventJournalTable.JournalId = journalTableData.nextJournalId();
inventJournalTable.JournalType = InventJournalType::LossProfit;
inventJournalTable.JournalNameId = journalTableData.journalStatic().standardJournalNameId(inventJournalTable.JournalType);
inventJournalTable.initFromInventJournalName(InventJournalName::find(inventJournalTable.JournalNameId));
inventJournalTable.Description = #Description;
if (inventJournalTable.validateWrite())
{
inventJournalTable.insert();
//Journal line
lineNum++;
journalTransData = journalTableData.journalStatic().newJournalTransData(inventJournalTrans, journalTableData);
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.InventSiteId = #Site;
inventDim.InventLocationId = #Warehouse;
inventJournalTrans.clear();
inventJournalTrans.initValue();
inventJournalTrans.initFromInventJournalTable(inventJournalTable);
inventJournalTrans.Qty = #Qty;
inventJournalTrans.setInventDimId(InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim).InventDimId);
inventJournalTrans.initFromInventTable(InventTable::find(#ItemId), false, false);
inventJournalTrans.LineNum = lineNum;
if (inventJournalTrans.validateWrite())
{
journalTransData.insert();
journalTableData.journalTable().update();
}
else
throw error("Journal line");
}
else
throw error("Journal header");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Please note that in this example I assign JournalId programmatically from respective Number sequence
Inventory journal header
Inventory journal lines
Inventory transactions
Voucher
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Inventory transactions. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Inventory transactions.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Customer Transactions Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Customer transactions.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. The structure of tables comprising Ledger journal header/lines and Customer transactions details didn't change, however the structure of tables for financial transactions did change significantly. The proven method to import financial transactions in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 is to import the data into Ledger journals and then validate/post the journals which will generate all necessary financial transactions.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (LedgerJournalTable, LedgerJournalTrans) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Vendor transactions. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
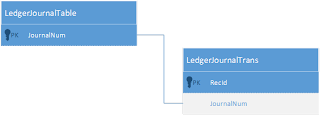
LedgerJournalTable
|
The LedgerJournalTable table contains all the defaulting and state information pertaining to a single journal. The transaction details of a journal are managed in the LedgerJournalTrans table.
|
LedgerJournalTrans
|
The LedgerJournalTrans table contains the transaction detail information that pertains to a single journal. The individual transaction lines are also referred to as voucher lines. The journal is a record in the LedgerJournalTable table.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromLedgerJournalName method on LedgerJournalTable table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void CustomerTransactionsXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Name("GenJrn")
#define.Num("AlexJrnC")
#define.Description("Alex Journal")
#define.Voucher("AlexC")
#define.Customer("US-001")
#define.OffsetAccount("999999")
#define.BusinessUnit("001")
#define.Department("022")
#define.CostCenter("007")
#define.ItemGroup("Audio")
#define.Text("Test")
#define.Currency("USD")
#define.Debit(100)
#define.Credit(0)
#define.Invoice("Invoice1")
LedgerJournalName ledgerJournalName;
LedgerJournalTable ledgerJournalTable;
LedgerJournalTrans ledgerJournalTrans;
try
{
ttsbegin;
ledgerJournalName = LedgerJournalName::find(#Name);
if (ledgerJournalName)
{
//Journal header
ledgerJournalTable.clear();
ledgerJournalTable.initValue();
ledgerJournalTable.initFromLedgerJournalName(ledgerJournalName.JournalName);
ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = #Num;
//ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = NumberSeq::newGetNum(LedgerParameters::numRefJournalNum()).num();
ledgerJournalTable.Name = #Description;
if (ledgerJournalTable.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTable.insert();
//Journal line
ledgerJournalTrans.clear();
ledgerJournalTrans.initValue();
ledgerJournalTrans.JournalNum = ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum;
ledgerJournalTrans.TransDate = systemDateGet();
ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = #Voucher;
//ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = NumberSeq::newGetVoucher(null).num();
//Vendor
ledgerJournalTrans.parmAccount(#Customer, LedgerJournalACType::Cust);
ledgerJournalTrans.parmDefaultDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getDimensionAttributeValueSetId(
[2, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department]));
//Offset Account
ledgerJournalTrans.OffsetAccountType = LedgerJournalACType::Ledger;
ledgerJournalTrans.parmOffsetLedgerDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getLedgerAccountId(
[strFmt("%1-%2-%3-%4-%5", #OffsetAccount, #BusinessUnit, #Department, #CostCenter, #ItemGroup),
#OffsetAccount, 4, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department, "CostCenter", #CostCenter, "ItemGroup", #ItemGroup]));
ledgerJournalTrans.Txt = #Text;
ledgerJournalTrans.CurrencyCode = #Currency;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurDebit = #Debit;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurCredit = #Credit;
ledgerJournalTrans.Invoice = #Invoice;
if (ledgerJournalTrans.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTrans.insert();
}
else
throw error("Journal line");
}
else
throw error("Journal header");
}
else
throw error("Journal name");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
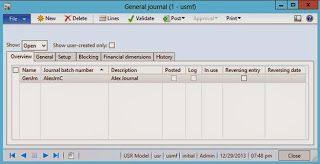
Result:
Number sequence
Please note that I marked "To a lower number" and "To a higher number" checkboxes for Journal batch number Number sequence in order to be able to assign JournalNum explicitly
Ledger journal header
Ledger journal lines
Ledger journal lines – Account – Dimensions
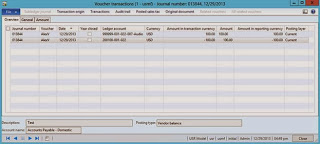
Voucher
Customer transactions
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Customer transactions. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Customer transactions.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Vendor Transactions Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Vendor transactions.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. The structure of tables comprising Ledger journal header/lines and Vendor transactions details didn't change, however the structure of tables for financial transactions did change significantly. The proven method to import financial transactions in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 is to import the data into Ledger journals and then validate/post the journals which will generate all necessary financial transactions.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (LedgerJournalTable, LedgerJournalTrans) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Vendor transactions. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
LedgerJournalTable
|
The LedgerJournalTable table contains all the defaulting and state information pertaining to a single journal. The transaction details of a journal are managed in the LedgerJournalTrans table.
|
LedgerJournalTrans
|
The LedgerJournalTrans table contains the transaction detail information that pertains to a single journal. The individual transaction lines are also referred to as voucher lines. The journal is a record in the LedgerJournalTable table.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromLedgerJournalName method on LedgerJournalTable table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void VendorTransactionsXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Name("GenJrn")
#define.Num("AlexJrnV")
#define.Description("Alex Journal")
#define.Voucher("AlexV")
#define.Vendor("US-101")
#define.OffsetAccount("999999")
#define.BusinessUnit("001")
#define.Department("022")
#define.CostCenter("007")
#define.ItemGroup("Audio")
#define.Text("Test")
#define.Currency("USD")
#define.Debit(0)
#define.Credit(100)
#define.Invoice("Invoice1")
LedgerJournalName ledgerJournalName;
LedgerJournalTable ledgerJournalTable;
LedgerJournalTrans ledgerJournalTrans;
try
{
ttsbegin;
ledgerJournalName = LedgerJournalName::find(#Name);
if (ledgerJournalName)
{
//Journal header
ledgerJournalTable.clear();
ledgerJournalTable.initValue();
ledgerJournalTable.initFromLedgerJournalName(ledgerJournalName.JournalName);
ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = #Num;
//ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = NumberSeq::newGetNum(LedgerParameters::numRefJournalNum()).num();
ledgerJournalTable.Name = #Description;
if (ledgerJournalTable.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTable.insert();
//Journal line
ledgerJournalTrans.clear();
ledgerJournalTrans.initValue();
ledgerJournalTrans.JournalNum = ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum;
ledgerJournalTrans.TransDate = systemDateGet();
ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = #Voucher;
//ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = NumberSeq::newGetVoucher(null).num();
//Vendor
ledgerJournalTrans.parmAccount(#Vendor, LedgerJournalACType::Vend);
ledgerJournalTrans.parmDefaultDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getDimensionAttributeValueSetId(
[4, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department, "CostCenter", #CostCenter,"ItemGroup", #ItemGroup]));
//Offset Account
ledgerJournalTrans.OffsetAccountType = LedgerJournalACType::Ledger;
ledgerJournalTrans.parmOffsetLedgerDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getLedgerAccountId(
[strFmt("%1-%2-%3-%4-%5", #OffsetAccount, #BusinessUnit, #Department, #CostCenter, #ItemGroup),
#OffsetAccount, 4, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department, "CostCenter", #CostCenter, "ItemGroup", #ItemGroup]));
ledgerJournalTrans.Txt = #Text;
ledgerJournalTrans.CurrencyCode = #Currency;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurDebit = #Debit;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurCredit = #Credit;
ledgerJournalTrans.Invoice = #Invoice;
if (ledgerJournalTrans.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTrans.insert();
}
else
throw error("Journal line");
}
else
throw error("Journal header");
}
else
throw error("Journal name");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Number sequence
Please note that I marked "To a lower number" and "To a higher number" checkboxes for Journal batch number Number sequence in order to be able to assign JournalNum explicitly
Ledger journal header
Ledger journal lines
Ledger journal lines – Account – Dimensions
Voucher
Vendor transactions
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Vendor transactions. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Vendor transactions.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp –
Ledger Transactions Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Ledger transactions.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. The structure of tables comprising Ledger journal header/lines didn't change, however the structure of tables for financial transactions did change significantly. The proven method to import financial transactions in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 is to import the data into Ledger journals and then validate/post the journals which will generate all necessary financial transactions.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (LedgerJournalTable, LedgerJournalTrans) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Ledger transactions. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
LedgerJournalTable
|
The LedgerJournalTable table contains all the defaulting and state information pertaining to a single journal. The transaction details of a journal are managed in the LedgerJournalTrans table.
|
LedgerJournalTrans
|
The LedgerJournalTrans table contains the transaction detail information that pertains to a single journal. The individual transaction lines are also referred to as voucher lines. The journal is a record in the LedgerJournalTable table.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromLedgerJournalName method on LedgerJournalTable table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
static void LedgerTransactionsXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.Name("GenJrn")
#define.Num("AlexJrn")
#define.Description("Alex Journal")
#define.Voucher("Alex")
#define.Account("110180")
#define.OffsetAccount("999999")
#define.BusinessUnit("001")
#define.Department("022")
#define.CostCenter("007")
#define.ItemGroup("Audio")
#define.Text("Test")
#define.Currency("USD")
#define.Debit(100)
#define.Credit(0)
LedgerJournalName ledgerJournalName;
LedgerJournalTable ledgerJournalTable;
LedgerJournalTrans ledgerJournalTrans;
try
{
ttsbegin;
ledgerJournalName = LedgerJournalName::find(#Name);
if (ledgerJournalName)
{
//Journal header
ledgerJournalTable.clear();
ledgerJournalTable.initValue();
ledgerJournalTable.initFromLedgerJournalName(ledgerJournalName.JournalName);
ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = #Num;
//ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum = NumberSeq::newGetNum(LedgerParameters::numRefJournalNum()).num();
ledgerJournalTable.Name = #Description;
if (ledgerJournalTable.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTable.insert();
//Journal line
ledgerJournalTrans.clear();
ledgerJournalTrans.initValue();
ledgerJournalTrans.JournalNum = ledgerJournalTable.JournalNum;
ledgerJournalTrans.TransDate = systemDateGet();
ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = #Voucher;
//ledgerJournalTrans.Voucher = NumberSeq::newGetVoucher(null).num();
ledgerJournalTrans.AccountType = LedgerJournalACType::Ledger;
ledgerJournalTrans.parmLedgerDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getLedgerAccountId(
[strFmt("%1-%2-%3", #Account, #BusinessUnit, #Department),
#Account, 2, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department]));
ledgerJournalTrans.OffsetAccountType = LedgerJournalACType::Ledger;
ledgerJournalTrans.parmOffsetLedgerDimension(AxdDimensionUtil::getLedgerAccountId(
[strFmt("%1-%2-%3-%4-%5", #OffsetAccount, #BusinessUnit, #Department, #CostCenter, #ItemGroup),
#OffsetAccount, 4, "BusinessUnit", #BusinessUnit, "Department", #Department, "CostCenter", #CostCenter, "ItemGroup", #ItemGroup]));
ledgerJournalTrans.Txt = #Text;
ledgerJournalTrans.CurrencyCode = #Currency;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurDebit = #Debit;
ledgerJournalTrans.AmountCurCredit = #Credit;
if (ledgerJournalTrans.validateWrite())
{
ledgerJournalTrans.insert();
}
else
throw error("Journal line");
}
else
throw error("Journal header");
}
else
throw error("Journal name");
ttscommit;
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Number sequence
Please note that I marked "To a lower number" and "To a higher number" checkboxes for Journal batch number Number sequence in order to be able to assign JournalNum explicitly
Ledger journal header
Ledger journal lines
Voucher
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company USMF) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM, R2
Summary: In this document I explained how to write a required minimum X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Ledger transactions. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach can be very handy for POC's or in situation with always changing requirements. You can also use Microsoft Dynamics AX Excel Add-in to import relatively small amounts of data. Please consider using DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. DIXF (Data Import Export Framework) provides a standard template for import of Ledger transactions.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp – Product Masters Import
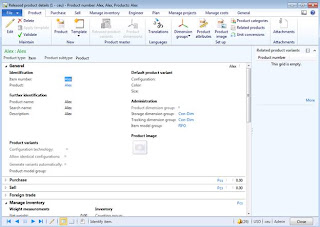
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Product masters and Released product variants.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. In order to create a product in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 both product definition and released product information will have to be provided. Please note that in Dynamics AX 2012 Rich Client product definition is automatically created when released product is created using decentralized approach. Also number of table records will have to be populated in order to create Product masters and Released product variants.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (EcoResProduct, EcoResProductMaster, EcoResDistinctProductVariant, InventTable, etc) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Product masters and Released product variants. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Assumption: The assumption is that appropriate reference data such as item groups, etc. was created in advance.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
EcoResProduct
|
The EcoResProduct table stores products and is the base table in the products hierarchy.
|
EcoResProductMaster
|
The EcoResProductMaster table stores product masters.
|
EcoResProductIdentifier
|
The EcoResProductIdentifier table contains a product identification that is available for users.
|
EcoResDistinctProduct
|
The EcoResDistinctProduct table stores products.
|
EcoResDistinctProductVariant
|
The EcoResDistinctProductVariant table stores product variants.
|
EcoResProductDimensionGroup
|
The EcoResProductDimensionGroup table contains information about a dimension group.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroup
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroup table contains information about a storage dimension group.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup table contains information about a tracking dimension group.
|
EcoResProductDimensionGroupProduct
|
The EcoResProductDimensionGroupProduct table stores information about relationships between products and dimension groups.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct table contains information about the associations between products and storage dimension groups.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct table contains information about the associations between products and tracking dimension groups.
|
EcoResColor
|
The EcoResColor table stores color names.
|
EcoResSize
|
The EcoResSize table stores size names.
|
EcoResConfiguration
|
The EcoResConfiguration table stores configuration names.
|
EcoResProductMasterColor
|
The EcoResProductMasterColor table stores information about colors assigned to product masters.
|
EcoResProductMasterSize
|
The EcoResProductMasterSize table stores information about sizes that are assigned to product masters.
|
EcoResProductMasterConfiguration
|
The EcoResProductMasterConfiguration table stores information about configurations assigned to product masters.
|
EcoResProductVariantColor
|
The EcoResProductVariantColor table stores information about the colors that are assigned to product variants.
|
EcoResProductVariantSize
|
The EcoResProductVariantSize table stores information about the sizes that are assigned to product variants.
|
EcoResProductVariantConfiguration
|
The EcoResProductVariantConfiguration table stores information about the configurations that are assigned to product variants.
|
EcoResProductMasterDimensionValue
|
The EcoResProductMasterDimensionValue table is the base table in the product model dimension hierarchy.
|
EcoResProductVariantDimensionValue
|
The EcoResProductVariantDimensionValue table is the base table in the product variant dimension hierarchy.
|
EcoResProductDimensionAttribute
|
The EcoResProductDimensionAttribute table contains definitions of product dimension attributes (categories).
|
EcoResInstanceValue
|
The EcoResInstanceValue table contains the definitions of the instances of the components or products.
|
EcoResProductInstanceValue
|
The EcoResProductInstanceValue table contains definitions of values for the instances of attributes of a product.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and storage dimension groups.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and tracking dimension groups.
|
InventTable
|
The InventTable table contains information about items.
|
InventTableModule
|
The InventTableModule table contains information about purchase, sales, and inventory specific settings for items.
|
InventItemLocation
|
The InventItemLocation table contains information about items and the related warehouse and counting settings. The settings can be made specific based on the items configuration and vary from warehouse to warehouse.
|
InventItemSalesSetup
|
The InventItemSalesSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to sales settings.
|
InventItemInventSetup
|
The InventItemInventSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to inventory settings.
|
InventItemPurchSetup
|
The InventItemPurchSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to purchase settings.
|
InventItemSetupSupplyType
|
The InventItemSetupSupplyType table contains information about the sourcing of items.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
InventModelGroupItem
|
The InventModelGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and item model groups.
|
InventItemGroupItem
|
The InventItemGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and item groups.
|
InventDimCombination
|
The InventDimCombination table contains variants of items. The variants are created as product variants that are based on product dimensions such as size, color, and configuration. These variants are replicated to the legal entity.
|
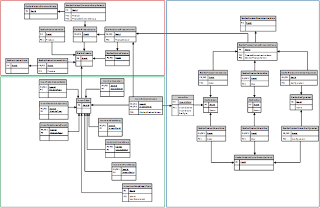
Data Model Diagram:
Zoom
Red area highlights tables forming Products and Product Masters data model
Green area highlights tables forming Released Products data models
Blue area highlights tables implementing Product Dimensions data model
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromEcoResProduct method on InventTable table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
Product masters and Released product variants
static void ProductMastersXppImport(Args _args)
{
EcoResProductMaster ecoResProductMaster;
EcoResProductIdentifier ecoResProductIdentifier;
EcoResProductDimensionGroupProduct ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct;
EcoResProductMasterModelingPolicy ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy;
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct;
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct;
EcoResConfiguration ecoResConfiguration;
EcoResProductMasterConfiguration ecoResProductMasterConfiguration;
EcoResDistinctProductVariant ecoResDistinctProductVariant;
EcoResProductVariantConfiguration ecoResProductVariantConfiguration;
InventTable inventTable;
InventTableModule inventTableModule;
InventItemSetupSupplyType inventItemSetupSupplyType;
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem;
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem;
InventModelGroupItem inventModelGroupItem;
InventItemGroupItem inventItemGroupItem;
InventDim inventDim;
InventDimCombination inventDimCombination;
try
{
//ProductMaster
ecoResProductMaster.clear();
ecoResProductMaster.initValue();
ecoResProductMaster.ProductType = EcoResProductType::Item;
ecoResProductMaster.DisplayProductNumber = "AlexMaster";
ecoResProductMaster.SearchName = "AlexMaster";
ecoResProductMaster.VariantConfigurationTechnology = EcoResVariantConfigurationTechnologyType::PredefinedVariants;
if (ecoResProductMaster.validateWrite())
{
ecoResProductMaster.insert();
ecoResProductIdentifier.clear();
ecoResProductIdentifier.initValue();
ecoResProductIdentifier.ProductNumber = "AlexMaster";
ecoResProductIdentifier.Product = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
ecoResProductIdentifier.insert();
//Product dimension group
ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.clear();
ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.initValue();
ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.initFromProduct(ecoResProductMaster);
ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.ProductDimensionGroup = EcoResProductDimensionGroup::findByDimensionGroupName("Con-Dim").RecId;
if (ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResProductDimensionGroupProduct.insert();
}
//Storage dimension group
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.clear();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.initValue();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.Product = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.StorageDimensionGroup = EcoResStorageDimensionGroup::findByDimensionGroupName("Con-Dim").RecId;
if (ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.insert();
}
//Tracking dimension group
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.clear();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.initValue();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.Product = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.TrackingDimensionGroup = EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup::findByDimensionGroupName("Con-Dim").RecId;
if (ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.insert();
}
//Product modeling policy
ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy.clear();
ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy.initValue();
ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy.ProductMaster = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
if (ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy.validateWrite())
{
ecoResProductMasterModelingPolicy.insert();
}
//Product translation
EcoResProductTranslation::createOrUpdateTranslation(ecoResProductMaster.RecId, "AlexMaster","AlexMaster");
//Configuration
ecoResConfiguration = EcoResConfiguration::findByName("Alex-1");
if (!ecoResConfiguration)
{
ecoResConfiguration.clear();
ecoResConfiguration.initValue();
ecoResConfiguration.Name = "Alex-1";
ecoResConfiguration.insert();
}
//Configuration assigned to product master
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.clear();
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.initValue();
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.Configuration = ecoResConfiguration.RecId;
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.Description = "Alex-1";
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.ConfigProductDimensionAttribute = EcoResProductDimensionAttribute::inventDimFieldId2DimensionAttributeRecId(fieldNum(InventDim, ConfigId));
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.ConfigProductMaster = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
ecoResProductMasterConfiguration.insert();
//Product variant
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.clear();
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.initValue();
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.DisplayProductNumber = EcoResProductNumberBuilderVariant::buildFromProductNumberAndDimensions(
ecoResProductMaster.productNumber(),
EcoResProductVariantDimValue::getDimensionValuesContainer("Alex-1", "", ""));
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.SearchName = ecoResProductMaster.SearchName + "Alex-1"/*ConfigId*/;
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.ProductType = ecoResProductMaster.ProductType;
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.ProductMaster = ecoResProductMaster.RecId;
ecoResDistinctProductVariant.insert();
//Product variant configuration
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.clear();
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.initValue();
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.initFromDistinctProductVariant(ecoResDistinctProductVariant);
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.ProductDimensionAttribute = EcoResProductDimensionAttribute::inventDimFieldId2DimensionAttributeRecId(fieldNum(InventDim, ConfigId));
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.Configuration = ecoResConfiguration.RecId;
ecoResProductVariantConfiguration.insert();
//Product variant translation
EcoResProductTranslation::createOrUpdateTranslation(ecoResDistinctProductVariant.RecId,"AlexMaster", "AlexMaster");
//Released product
inventTable.clear();
inventTable.initValue();
inventTable.initFromEcoResProduct(ecoResProductMaster);
inventTable.ItemId = "AlexMaster";
inventTable.NameAlias = "AlexMaster";
if (inventTable.validateWrite())
{
inventTable.insert();
//Inventory model group
inventModelGroupItem.clear();
inventModelGroupItem.initValue();
inventModelGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.dataAreaId;
inventModelGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventModelGroupItem.ModelGroupId = "FIFO";
inventModelGroupItem.ModelGroupDataAreaId = curext();
inventModelGroupItem.insert();
//Item group
inventItemGroupItem.clear();
inventItemGroupItem.initValue();
inventItemGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.dataAreaId;
inventItemGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventItemGroupItem.ItemGroupId = "Parts";
inventItemGroupItem.ItemGroupDataAreaId = curext();
inventItemGroupItem.insert();
//Extended product details - Inventory
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Invent;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Extended product details - Purchase
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Purch;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Extended product details - Sales
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Sales;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Warehouse items
InventItemLocation::createDefault(inventTable.ItemId);
//Supply type setup
inventItemSetupSupplyType.clear();
inventItemSetupSupplyType.initValue();
inventItemSetupSupplyType.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventItemSetupSupplyType.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
inventItemSetupSupplyType.insert();
//Product storage dimension group
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct = EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct::findByProduct(ecoResProductMaster.RecId);
if (ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.RecId)
{
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.clear();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.initValue();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.StorageDimensionGroup = ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.StorageDimensionGroup;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.insert();
}
//Product tracking dimension group
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct = EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct::findByProduct(ecoResProductMaster.RecId);
if (ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.RecId)
{
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.clear();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.initValue();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.TrackingDimensionGroup = ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.TrackingDimensionGroup;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.insert();
}
}
inventDim.clear();
inventDim.ConfigId = "Alex-1";/*ConfigId*/
inventDim = InventDim::findOrCreate(inventDim);
//Released product variant
inventDimCombination.clear();
inventDimCombination.initValue();
inventDimCombination.DistinctProductVariant = ecoResDistinctProductVariant.RecId;
inventDimCombination.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventDimCombination.InventDimId = inventDim.InventDimId;
inventDimCombination.insert();
}
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Product master
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Product variant
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Released product
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Released product variant
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company CEU) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM
Summary: In this document I explained how to write X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Product masters and Released products variants. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach allows getting better performance during the import comparing to usage of Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Excel Add-in. Also this approach is more flexible for extending in the case of not yet fully defined or changing business requirements. Please consider using Data Import/Export Framework (former DMF, Data Migration Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. Data Import/Export Framework provides a standard template for import of Product Masters.
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Xpp – Products Import
Purpose: The purpose of this document is to illustrate how to write X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Products and Released products.
Challenge: Data model changes in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 related to high normalization and introduction of surrogate keys made some imports more complex. In order to create a product in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 both product definition and released product information will have to be provided. Please note that in Dynamics AX 2012 Rich Client product definition is automatically created when released product is created using decentralized approach.
Solution: Appropriate tables buffers (EcoResProduct, EcoResDistinctProduct, InventTable, etc) will be used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Products and Released products. Alternatively AxBC classes may be used instead of table buffers.
Assumption: The assumption is that appropriate reference data such as item groups, etc. was created in advance.
Data Model:
Table Name
|
Table Description
|
EcoResProduct
|
The EcoResProduct table stores products and is the base table in the products hierarchy.
|
EcoResProductIdentifier
|
The EcoResProductIdentifier table contains a product identification that is available for users.
|
EcoResDistinctProduct
|
The EcoResDistinctProduct table stores products.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroup
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroup table contains information about a storage dimension group.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup table contains information about a tracking dimension group.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct table contains information about the associations between products and storage dimension groups.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct table contains information about the associations between products and tracking dimension groups.
|
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem
|
The EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and storage dimension groups.
|
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem
|
The EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and tracking dimension groups.
|
InventTable
|
The InventTable table contains information about items.
|
InventTableModule
|
The InventTableModule table contains information about purchase, sales, and inventory specific settings for items.
|
InventItemLocation
|
The InventItemLocation table contains information about items and the related warehouse and counting settings. The settings can be made specific based on the items configuration and vary from warehouse to warehouse.
|
InventItemSalesSetup
|
The InventItemSalesSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to sales settings.
|
InventItemInventSetup
|
The InventItemInventSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to inventory settings.
|
InventItemPurchSetup
|
The InventItemPurchSetup table contains the default settings for items, such as site and warehouse. The values are related to purchase settings.
|
InventItemSetupSupplyType
|
The InventItemSetupSupplyType table contains information about the sourcing of items.
|
InventModelGroupItem
|
The InventModelGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and item model groups.
|
InventItemGroupItem
|
The InventItemGroupItem table contains information about the associations between items and item groups.
|
InventDim
|
The InventDim table contains values for inventory dimensions.
|
Data Model Diagram:
Zoom
Red area highlights tables forming Products and Product Masters data model
Green area highlights tables forming Released Products data models
Blue area highlights tables implementing Product Dimensions data model
Development:
ttsBegin: Use ttsBegin to start a transaction.
clear: The clear method clears the contents of the record.
initValue: The initValue method initializes the fields of the record.
initFrom*: The initFrom* methods usually populate the fields of the child record based on the fields on the parent record. Example is initFromEcoResProduct method on InventTable table.
validateWrite: The validateWrite method checks whether the record can be written.
write: The write method writes the record to the database.
insert: The insert method inserts the record into the database.
doInsert: The doInsert method inserts the record into the database. Calling doInsert ensures that any X++ code written in the insert method of the record is not executed. Calling insert always executes the X++ code written in the insertmethod of the record.
ttsCommit: Use ttsCommit to commit a transaction.
Source code:
Products and Released products
static void ProductsXppImport(Args _args)
{
#define.ProductNum()
#define.SearchName()
#define.StorageDim()
#define.TrackingDim()
#define.ItemId()
#define.NameAlias()
#define.ModelGroup()
#define.ItemGroup()
EcoResDistinctProduct ecoResDistinctProduct;
EcoResProductIdentifier ecoResProductIdentifier;
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct;
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct;
InventTable inventTable;
InventTableModule inventTableModule;
InventItemSetupSupplyType inventItemSetupSupplyType;
EcoResStorageDimensionGroupItem ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem;
EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem;
InventModelGroupItem inventModelGroupItem;
InventItemGroupItem inventItemGroupItem;
try
{
//Product
ecoResDistinctProduct.clear();
ecoResDistinctProduct.initValue();
ecoResDistinctProduct.ProductType = EcoResProductType::Item;
ecoResDistinctProduct.DisplayProductNumber = "Alex";
ecoResDistinctProduct.SearchName = "Alex";
if (ecoResDistinctProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResDistinctProduct.insert();
ecoResProductIdentifier.clear();
ecoResProductIdentifier.initValue();
ecoResProductIdentifier.ProductNumber = "Alex";
ecoResProductIdentifier.Product = ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId;
ecoResProductIdentifier.insert();
//Storage dimension group
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.clear();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.initValue();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.Product = ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.StorageDimensionGroup = EcoResStorageDimensionGroup::findByDimensionGroupName("Con-Dim").RecId;
if (ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.insert();
}
//Tracking dimension group
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.clear();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.initValue();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.Product = ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.TrackingDimensionGroup = EcoResTrackingDimensionGroup::findByDimensionGroupName("Con-Dim").RecId;
if (ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.validateWrite())
{
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.insert();
}
EcoResProductTranslation::createOrUpdateTranslation(ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId, "Alex", "Alex");
//Released product
inventTable.clear();
inventTable.initValue();
inventTable.initFromEcoResProduct(ecoResDistinctProduct);
inventTable.ItemId = "Alex";
inventTable.NameAlias = "Alex";
if (inventTable.validateWrite())
{
inventTable.insert();
//Inventory model group
inventModelGroupItem.clear();
inventModelGroupItem.initValue();
inventModelGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.dataAreaId;
inventModelGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventModelGroupItem.ModelGroupId = "FIFO";
inventModelGroupItem.ModelGroupDataAreaId = curext();
inventModelGroupItem.insert();
//Item group
inventItemGroupItem.clear();
inventItemGroupItem.initValue();
inventItemGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.dataAreaId;
inventItemGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventItemGroupItem.ItemGroupId = "Parts";
inventItemGroupItem.ItemGroupDataAreaId = curext();
inventItemGroupItem.insert();
//Extended product details - Inventory
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Invent;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Extended product details - Purchase
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Purch;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Extended product details - Sales
inventTableModule.clear();
inventTableModule.initValue();
inventTableModule.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventTableModule.ModuleType = ModuleInventPurchSales::Sales;
inventTableModule.insert();
//Warehouse items
InventItemLocation::createDefault(inventTable.ItemId);
//Supply type setup
inventItemSetupSupplyType.clear();
inventItemSetupSupplyType.initValue();
inventItemSetupSupplyType.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
inventItemSetupSupplyType.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
inventItemSetupSupplyType.insert();
//Product storage dimension group
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct = EcoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct::findByProduct(ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId);
if (ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.RecId)
{
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.clear();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.initValue();
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.StorageDimensionGroup = ecoResStorageDimensionGroupProduct.StorageDimensionGroup;
ecoResStorageDimensionGroupItem.insert();
}
//Product tracking dimension group
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct = EcoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct::findByProduct(ecoResDistinctProduct.RecId);
if (ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.RecId)
{
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.clear();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.initValue();
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.ItemDataAreaId = inventTable.DataAreaId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.ItemId = inventTable.ItemId;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.TrackingDimensionGroup = ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupProduct.TrackingDimensionGroup;
ecoResTrackingDimensionGroupItem.insert();
}
}
}
}
catch
{
error("Error!");
return;
}
info("Done!");
}
|
Result:
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Product
Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 – Released product
Note: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Demo Data (Company CEU) was used for this example
Version: Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 RTM
Summary: In this document I explained how to write X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 in order to import Products and Released products. Appropriate table buffers were used when writing X++ code in Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012. This approach allows getting better performance during the import comparing to usage of Microsoft Dynamics AX 2012 Excel Add-in. Also this approach is more flexible for extending in the case of not yet fully defined or changing business requirements. Please consider using Data Import/Export Framework (former DMF, Data Migration Framework) for import of significant amounts of data when performance is an important consideration. Data Import/Export Framework provides a standard template for import of Products.